The Amygdala and it's Link to BPD
/The Amygdala is a small region of the brain which plays a key role in emotional regulation, emotional memory and responses to emotional stimuli.
Recent technological advances have given neurologists two new ways to create 3-D images of the brain. These techniques are known as Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scanning) and functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). By scanning a person's brain while prompting them to think in a certain way, scientists are unlocking clues as to which regions of the brain are responsible for different kinds of thought.
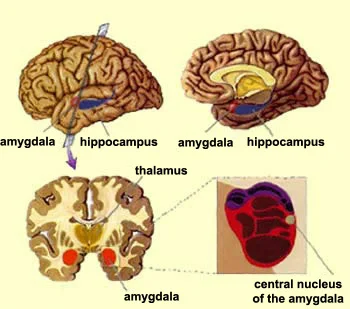
Much of this work has focused on the amygdala - a small region deep in the brain shown below. There is one amygdala the right side of the brain and one on the left.
The Amygdala, courtesy The Brain From Top To Bottom @ http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/
The Amygdala's Role in Emotional Reactions
It is believed that the amygdala has an important rule in producing lightning-fast emotional responses to events, whenever a person recognizes an event with a strong emotional element (good or bad) such as events that results in fear, anger or rage or events that result in delight, joy or excitement.
The amygdala is believed to be part of our fast, instinctive and reactive brains. Not much conscious thought is involved if an object is hurled towards us and we instinctively duck. This ability to react instinctively to danger is thought to have historically played a critical function in survival of most species. Similarly, witness the reaction of a crowd whenever a sports team scores a goal. There is a universal instant response of throwing hands in the air, widening the eyes, leaping into the air etc, without much thought given. When you see these instinctive reactions occur, the amygdala is at work.
The Amygdala and Memory
The amygdala has also been shown to have an important function in enhancing memory functions by releasing stress hormones, such as adrenaline. It has been shown experimentally that rats, who have had their amygdala disabled lose their fear of cats. It has also been shown that increasing stress hormones improves memory of an event. This helps explain why people can remember stressful moments in great detail - such as times of disasters or crises, when adrenaline is released and yet can easily forget long periods when nothing significant seems to have happened.
Gender Differences in the Way the Amygdala is Connected
Another interesting finding resulted from a study comparing amygdala activity in males and females. When shown images containing strong emotionally arousing content, it was found that the amygdala on the right side of the brain was the most active in men, while the amygdala on the left side of the brain was most active in women.
Other experiments with people who are relaxing have shown that in men, the right amygdala is more closely connected to the rest of the brain than the left, while women show a stronger connectivity between the left amygdala and the rest of the brain. Additionally, in men the right amygdala seems to be strongly connected to regions of the brain normally associated with interactions with the external environment while in women, the left amygdala seems to be strongly connected to regions of the brain normally associated with more internal thought. This suggests that in an emotional context, men are biased toward thoughts about the external environment and women toward thoughts about the internal environment.
The Link between the Amygdala and Emotional Regulation Disorder / Borderline Personality Disorder
In a famous experiment at Yale University, 15 people diagnosed with BPD and 15 people with no BPD diagnosis were shown photographs of faces with neutral, happy, sad, and fearful facial expressions while mapping the activity in the brain using fMRI. It was found that there is a lot more activity in the left amygdala of people who had been diagnosed with Borderline Personality Disorder when exposed to an emotional stimulus than there is for most other people.
Source: Donegan et al, Amygdala hyperreactivity in borderline personality disorder: implications for emotional dysregulation.